基本思想
快速排序采用的是分治思想,即在一个无序的序列中选取一个任意的基准元素pivot,利用pivot将待排序的序列分成两部分,前面部分元素均小于或等于基准元素,后面部分均大于或等于基准元素,然后采用递归的方法分别对前后两部分重复上述操作,直到将无序序列排列成有序序列。5
排序流程
快速排序算法通过多次比较和交换来实现排序,其排序流程如下:2
1、首先设定一个分界值,通过该分界值将数组分成左右两部分。2
2、将大于或等于分界值的数据集中到数组右边,小于分界值的数据集中到数组的左边。此时,左边部分中各元素都小于分界值,而右边部分中各元素都大于或等于分界值。2
3、然后,左边和右边的数据可以独立排序。对于左侧的数组数据,又可以取一个分界值,将该部分数据分成左右两部分,同样在左边放置较小值,右边放置较大值。右侧的数组数据也可以做类似处理。2
4、重复上述过程,可以看出,这是一个递归定义。通过递归将左侧部分排好序后,再递归排好右侧部分的顺序。当左、右两个部分各数据排序完成后,整个数组的排序也就完成了。2
排序步骤
原理
设要排序的数组是A[0]……A[N-1],首先任意选取一个数据(通常选用数组的第一个数)作为关键数据,然后将所有比它小的数都放到它左边,所有比它大的数都放到它右边,这个过程称为一趟快速排序。值得注意的是,快速排序不是一种稳定的排序算法,也就是说,多个相同的值的相对位置也许会在算法结束时产生变动。1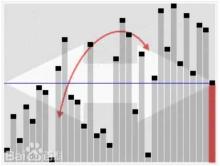
一趟快速排序的算法是:1
(1)设置两个变量i、j,排序开始的时候:i=0,j=N-1;1
(2)以第一个数组元素作为关键数据,赋值给key,即key=A[0];1
(3)从j开始向前搜索,即由后开始向前搜索(j--),找到第一个小于key的值A[j],将A[j]和A[i]的值交换;1
(4)从i开始向后搜索,即由前开始向后搜索(i++),找到第一个大于key的A[i],将A[i]和A[j]的值交换;1
(5)重复第3、4步,直到i==j; (3,4步中,没找到符合条件的值,即3中A[j]不小于key,4中A[i]不大于key的时候改变j、i的值,使得j=j-1,i=i+1,直至找到为止。找到符合条件的值,进行交换的时候i, j指针位置不变。另外,i==j这一过程一定正好是i+或j-完成的时候,此时令循环结束)。1
排序演示
假设一开始序列{xi}是:5,3,7,6,4,1,0,2,9,10,8。
此时,ref=5,i=1,j=11,从后往前找,第一个比5小的数是x8=2,因此序列为:2,3,7,6,4,1,0,5,9,10,8。
此时i=1,j=8,从前往后找,第一个比5大的数是x3=7,因此序列为:2,3,5,6,4,1,0,7,9,10,8。
此时,i=3,j=8,从第8位往前找,第一个比5小的数是x7=0,因此:2,3,0,6,4,1,5,7,9,10,8。
此时,i=3,j=7,从第3位往后找,第一个比5大的数是x4=6,因此:2,3,0,5,4,1,6,7,9,10,8。
此时,i=4,j=7,从第7位往前找,第一个比5小的数是x6=1,因此:2,3,0,1,4,5,6,7,9,10,8。
此时,i=4,j=6,从第4位往后找,直到第6位才有比5大的数,这时,i=j=6,ref成为一条分界线,它之前的数都比它小,之后的数都比它大,对于前后两部分数,可以采用同样的方法来排序。3
程序调用举例
用法:3
<pre data-lang="clike">void qsort(void *base, int nelem, int width, int (*fcmp)(const void *,const void *));
参数:
1、待排序数组首地址;3
2、数组中待排序元素数量;3
3、各元素的占用空间大小;3
4、指向函数的指针,用于确定排序的顺序。3
示例代码
GO
<pre data-lang="cpp">// 第一种写法func quickSort(values []int, left, right int) { temp := values[left] p := left i, j := left, right for i <= j { for j >= p && values[j] >= temp { j-- } if j >= p { values[p] = values[j] p = j } for i <= p && values[i] <= temp { i++ } if i <= p { values[p] = values[i] p = i } } values[p] = temp if p-left > 1 { quickSort(values, left, p-1) } if right-p > 1 { quickSort(values, p+1, right) }}func QuickSort(values []int) { if len(values) <= 1 { return } quickSort(values, 0, len(values)-1)}// 第二种写法func Quick2Sort(values []int) { if len(values) <= 1 { return } mid, i := values[0], 1 head, tail := 0, len(values)-1 for head < tail { fmt.Println(values) if values[i] > mid { values[i], values[tail] = values[tail], values[i] tail-- } else { values[i], values[head] = values[head], values[i] head++ i++ } } values[head] = mid Quick2Sort(values[:head]) Quick2Sort(values[head+1:])}// 第三种写法func Quick3Sort(a []int,left int, right int) { if left >= right { return } explodeIndex := left for i := left + 1; i <= right ; i++ { if a[left] >= a[i]{ //分割位定位++ explodeIndex ++; a[i],a[explodeIndex] = a[explodeIndex],a[i] } } //起始位和分割位 a[left], a[explodeIndex] = a[explodeIndex],a[left] Quick3Sort(a,left,explodeIndex - 1) Quick3Sort(a,explodeIndex + 1,right)}
Ruby
<pre data-lang="ruby">def quick_sort(a) (x=a.pop) ? quick_sort(a.select { |i| i <= x }) + [x] + quick_sort(a.select { |i| i > x }) : []end
Erlang语言
<pre data-lang="erlang">超简短实现:q_sort([])->[];q_sort([H|R])->q_sort([X||X<-R,X<H])++[H]++q_sort([X||X<-R,X>=H]).
Haskell语言
<pre data-lang="erlang">q_sort n=case n of []->[] (x:xs)->q_sort [a|a<-xs,a<=x]++[x]++q_sort [a|a<-xs,a>x]
C++语言
<pre data-lang="cpp">#include <iostream>using namespace std;void Qsort(int arr[], int low, int high){ if (high <= low) return; int i = low; int j = high; int key = arr[low]; while (true) { /*从左向右找比key大的值*/ while (arr[i] <= key) { i++; if (i == high){ break; } } /*从右向左找比key小的值*/ while (arr[j] >= key) { j--; if (j == low){ break; } } if (i >= j) break; /*交换i,j对应的值*/ int temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = temp; } /*中枢值与j对应值交换*/ arr[low] = arr[j]; arr[j] = key; Qsort(arr, low, j - 1); Qsort(arr, j + 1, high);}int main(){ int a[] = {57, 68, 59, 52, 72, 28, 96, 33, 24}; Qsort(a, 0, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]) - 1);/*这里原文第三个参数要减1否则内存越界*/ for(int i = 0; i < sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]); i++) { cout << a[i] << " "; } return 0;}/*参考数据结构p274(清华大学出版社,严蔚敏)*/
C语言版本
<pre data-lang="cpp">void quickSort(int *number, int first, int last) {int i, j, pivot;int temp;if (first<last) {pivot = first;i = first;j = last;while (i<j) {while (number[i] <= number[pivot] && i<last)i++;while (number[j]>number[pivot])j--;if (i<j) {temp = number[i];number[i] = number[j];number[j] = temp;}}temp = number[pivot];number[pivot] = number[j];number[j] = temp;quickSort(number, first, j - 1);quickSort(number, j + 1, last);}}
Swift
<pre data-lang="cpp">func quickSort(a: inout [Int], low: Int, high: Int) { if low >= high { // 递归结束条件 return } var i = low var j = high let key = a[i] while i < j { // 从右边开始比较,比key大的数位置不变 while i < j && a[j] >= key { j -= 1 } // 只要出现一个比key小的数,将这个数放入左边i的位置 a[i] = a[j] // 从左边开始比较,比key小的数位置不变 while i < j && a[i] <= key { i += 1 } // 只要出现一个比key大的数,将这个数放入右边j的位置 a[j] = a[i] } a[i] = key // 将key放入i的位置,则左侧数都比key小,右侧数都比key大 quickSort(a: &a, low: low, high: i - 1) // 左递归 quickSort(a: &a, low: i + 1, high: high) // 右递归}// 示例var m = [2,3,5,7,1,4,6,15,5,2,7,9,10,15,9,17,12]quickSort(a: &m, low: 0, high: m.count - 1)print(m)// 结果:[1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5, 6, 7, 7, 9, 9, 10, 12, 15, 15, 17]
Objective-C
<pre data-lang="cpp">+ (void)quickSort:(NSMutableArray *)m low:(int)low high:(int)high{ if (low >= high) { return; } int i = low; int j = high; id key = m[i]; while (i<j) { while (i<j && [m[j] intValue] >= [key intValue]) { j--; } if (i == j) { // 当key是目前最小的数时,会出现i=j的情况, break; } m[i++] = m[j]; // i++ 会减少一次m[i]和key的比较 while (i < j && [m[i] intValue] <= [key intValue]) { i++; } if (i == j) { // 当key是目前最大的数时(m[j]的前面),会出现i=j的情况 break; } m[j--] = m[i]; //j-- 会减少一次m[j]和key的比较 } m[i] = key; [self quickSort: m low: low high: i-1]; [self quickSort: m low: i+1 high: high]; // NSLog(@"快速排序 %@",m);}
JavaScript
<pre data-lang="js">const quickSort = (array) => { const sort = (arr, left = 0, right = arr.length - 1) => { if (left >= right) {//如果左边的索引大于等于右边的索引说明整理完毕 return } let i = left let j = right const baseVal = arr[j] // 取无序数组最后一个数为基准值 while (i < j) {//把所有比基准值小的数放在左边大的数放在右边 while (i < j && arr[i] <= baseVal) { //找到一个比基准值大的数交换 i++ } arr[j] = arr[i] // 将较大的值放在右边如果没有比基准值大的数就是将自己赋值给自己(i 等于 j) while (j > i && arr[j] >= baseVal) { //找到一个比基准值小的数交换 j-- } arr[i] = arr[j] // 将较小的值放在左边如果没有找到比基准值小的数就是将自己赋值给自己(i 等于 j) } arr[j] = baseVal // 将基准值放至中央位置完成一次循环(这时候 j 等于 i ) sort(arr, left, j-1) // 将左边的无序数组重复上面的操作 sort(arr, j+1, right) // 将右边的无序数组重复上面的操作 } const newArr = array.concat() // 为了保证这个函数是纯函数拷贝一次数组 sort(newArr) return newArr}// 方法二:let _quickSort = (left, right, nums) => { let swap = (left, right, nums) => { let temp = nums[left] nums[left] = nums[right] nums[right] = temp } if (left <= right) { let val = nums[left] let [i, j] = [left, right] while (i < j) { while (i < j && nums[j] > val) { j-- } while (i < j && nums[i] < val) { i++ } if (i < j) { swap(i, j , nums) } } nums[i] = val _quickSort(left, i - 1, nums) _quickSort(i + 1, right, nums) }}let quickSort = (...numbers) => { _quickSort(0, numbers.length - 1, numbers) return numbers}console.log(quickSort(1, 20, 9, 13, 59, 19, 98))
Java
<pre data-lang="java">/** * 入口函数(递归方法),算法的调用从这里开始。 */public void quickSort(int[] arr, int startIndex, int endIndex) { if (startIndex >= endIndex) { return; } // 核心算法部分:分别介绍 双边指针(交换法),双边指针(挖坑法),单边指针 int pivotIndex = doublePointerSwap(arr, startIndex, endIndex); // int pivotIndex = doublePointerHole(arr, startIndex, endIndex); // int pivotIndex = singlePointer(arr, startIndex, endIndex); // 用分界值下标区分出左右区间,进行递归调用 quickSort(arr, startIndex, pivotIndex - 1); quickSort(arr, pivotIndex + 1, endIndex);}/** * 双边指针(交换法) * 思路: * 记录分界值 pivot,创建左右指针(记录下标)。 * (分界值选择方式有:首元素,随机选取,三数取中法) * * 首先从右向左找出比pivot小的数据, * 然后从左向右找出比pivot大的数据, * 左右指针数据交换,进入下次循环。 * * 结束循环后将当前指针数据与分界值互换, * 返回当前指针下标(即分界值下标) */private int doublePointerSwap(int[] arr, int startIndex, int endIndex) { int pivot = arr[startIndex]; int leftPoint = startIndex; int rightPoint = endIndex; while (leftPoint < rightPoint) { // 从右向左找出比pivot小的数据 while (leftPoint < rightPoint && arr[rightPoint] > pivot) { rightPoint--; } // 从左向右找出比pivot大的数据 while (leftPoint < rightPoint && arr[leftPoint] <= pivot) { leftPoint++; } // 没有过界则交换 if (leftPoint < rightPoint) { int temp = arr[leftPoint]; arr[leftPoint] = arr[rightPoint]; arr[rightPoint] = temp; } } // 最终将分界值与当前指针数据交换 arr[startIndex] = arr[rightPoint]; arr[rightPoint] = pivot; // 返回分界值所在下标 return rightPoint;}/** * 双边指针(挖坑法) * 思路: * 创建左右指针。 * 记录左指针数据为分界值 pivot, * 此时左指针视为"坑",里面的数据可以被覆盖。 * * 首先从右向左找出比pivot小的数据, * 找到后立即放入左边坑中,当前位置变为新的"坑", * 然后从左向右找出比pivot大的数据, * 找到后立即放入右边坑中,当前位置变为新的"坑", * * 结束循环后将最开始存储的分界值放入当前的"坑"中, * 返回当前"坑"下标(即分界值下标) */private int doublePointerHole(int[] arr, int startIndex, int endIndex) { int pivot = arr[startIndex]; int leftPoint = startIndex; int rightPoint = endIndex; while (leftPoint < rightPoint) { // 从右向左找出比pivot小的数据, while (leftPoint < rightPoint && arr[rightPoint] > pivot) { rightPoint--; } // 找到后立即放入左边坑中,当前位置变为新的"坑" if (leftPoint < rightPoint) { arr[leftPoint] = arr[rightPoint]; leftPoint++; } // 从左向右找出比pivot大的数据 while (leftPoint < rightPoint && arr[leftPoint] <= pivot) { leftPoint++; } // 找到后立即放入右边坑中,当前位置变为新的"坑" if (leftPoint < rightPoint) { arr[rightPoint] = arr[leftPoint]; rightPoint--; } } // 将最开始存储的分界值放入当前的"坑"中 arr[rightPoint] = pivot; return rightPoint;}/** * 单边指针 * 思路: * 记录首元素为分界值 pivot, 创建标记 mark 指针。 * 循环遍历与分界值对比。 * 比分界值小,则 mark++ 后与之互换。 * 结束循环后,将首元素分界值与当前mark互换。 * 返回 mark 下标为分界值下标。 */private int singlePointer(int[] arr, int startIndex, int endIndex) { int pivot = arr[startIndex]; int markPoint = startIndex; for (int i = startIndex + 1; i <= endIndex; i++) { // 如果比分界值小,则 mark++ 后互换。 if (arr[i] < pivot) { markPoint++; int temp = arr[markPoint]; arr[markPoint] = arr[i]; arr[i] = temp; } } // 将首元素分界值与当前mark互换 arr[startIndex] = arr[markPoint]; arr[markPoint] = pivot; return markPoint;}
C#
<pre data-lang="c#"> using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace test{ class QuickSort { static void Main(string[] args) { int[] array = { 49, 38, 65, 97, 76, 13, 27 }; sort(array, 0, array.Length - 1); Console.ReadLine(); } /**一次排序单元,完成此方法,key左边都比key小,key右边都比key大。 **@param array排序数组 **@param low排序起始位置 **@param high排序结束位置 **@return单元排序后的数组 */ private static int sortUnit(int[] array, int low, int high) { int key = array[low]; while (low < high) { /*从后向前搜索比key小的值*/ while (array[high] >= key && high > low) --high; /*比key小的放左边*/ array[low] = array[high]; /*从前向后搜索比key大的值,比key大的放右边*/ while (array[low] <= key && high > low) ++low; /*比key大的放右边*/ array[high] = array[low]; } /*左边都比key小,右边都比key大。//将key放在游标当前位置。//此时low等于high */ array[low] = key; foreach (int i in array) { Console.Write("{0}\t", i); } Console.WriteLine(); return high; } /**快速排序 *@paramarry *@return */ public static void sort(int[] array, int low, int high) { if (low >= high) return; /*完成一次单元排序*/ int index = sortUnit(array, low, high); /*对左边单元进行排序*/ sort(array, low, index - 1); /*对右边单元进行排序*/ sort(array, index + 1, high); } }}
运行结果:27 38 13 49 76 97 65
13 27 38 49 76 97 65
13 27 38 49 65 76 97
快速排序就是递归调用此过程——在以49为中点分割这个数据序列,分别对前面一部分和后面一部分进行类似的快速排序,从而完成全部数据序列的快速排序,最后把此数据序列变成一个有序的序列,根据这种思想对于上述数组A的快速排序的全过程如图6所示:
初始状态 {49 38 65 97 76 13 27} 进行一次快速排序之后划分为 {27 38 13} 49 {76 97 65} 分别对前后两部分进行快速排序{27 38 13} 经第三步和第四步交换后变成 {13 27 38} 完成排序。{76 97 65} 经第三步和第四步交换后变成 {65 76 97} 完成排序。图示
F#
<pre data-lang="scala">let rec qsort = function [] -> [] |x::xs -> qsort [for i in xs do if i < x then yield i]@ x::qsort [for i in xs do if i >= x then yield i]
PHP
<pre data-lang="php"><?php$arr = array(25,133,452,364,5876,293,607,365,8745,534,18,33);function quick_sort($arr){ // 判断是否需要继续 if (count($arr) <= 1) { return $arr; } $middle = $arr[0]; // 中间值 $left = array(); // 小于中间值 $right = array();// 大于中间值 // 循环比较 for ($i=1; $i < count($arr); $i++) { if ($middle < $arr[$i]) { // 大于中间值 $right[] = $arr[$i]; } else { // 小于中间值 $left[] = $arr[$i]; } } // 递归排序两边 $left = quick_sort($left); $right = quick_sort($right); // 合并排序后的数据,别忘了合并中间值 return array_merge($left, array($middle), $right);}var_dump($arr);var_dump(quick_sort($arr));
Pascal
<pre data-lang="delphi">这里是完全程序,过程部分为快排program qsort;var n,p:integer; a:array[0..100000] of integer;procedure qs(l,r:integer);//假设被排序的数组是a,且快排后按升序排列)var i,j,m,t:integer;begin i:=l; j:=r;//(l(left),r(right)表示快排的左右区间) m:=a[(l+r)div2];//注意:本句不能写成:m:=(l+r)div2; repeat while a[i]<m do inc(i); while a[j]>m do dec(j);//若是降序把'<'与‘>'互换; if i<=j then begin t:=a[i]; a[i]:=a[j]; a[j]:=t; inc(i); dec(j); end; until i>j; if l<j then qs(l,j);//递归查找左区间 if i<r then qs(i,r);//递归查找右区间end;begin readln(n);//有n个数据要处理 for p:=1 to n do read(a[p]);//输入数据 qs(1,n); for p:=1 to n do write(a[p],'');//输出快排后的数据end.或者procedure quickSort(var a:array of integer;l,r:Integer);var i,j,x:integer;begin if l>=r then exit; i:=l; j:=r; x:=a[i]; while i<=j do begin while (i<j)and(a[j]>x) do dec(j); if i<j then begin a[i]:=a[j]; inc(i); end; while (i<j)and(a[i]<x) do inc(i); if i<j then begin a[j]:=a[i]; dec(j); end; a[i]:=x; quicksort(a,l,i-1); quicksort(a,i+1,r); end;end;
Python3:分而治之+递归
<pre data-lang="ruby">def quick_sort(data): """快速排序""" if len(data) >= 2: # 递归入口及出口 mid = data[len(data)//2] # 选取基准值,也可以选取第一个或最后一个元素 left, right = [], [] # 定义基准值左右两侧的列表 data.remove(mid) # 从原始数组中移除基准值 for num in data: if num >= mid: right.append(num) else: left.append(num) return quick_sort(left) + [mid] + quick_sort(right) else: return data# 示例:array = [2,3,5,7,1,4,6,15,5,2,7,9,10,15,9,17,12]print(quick_sort(array))# 输出为[1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5, 6, 7, 7, 9, 9, 10, 12, 15, 15, 17]
Rust
<pre data-lang="clike">fn quick_sort<T: PartialOrd + Copy>(list: &mut Vec<T>) -> &mut Vec<T> { if list.len() > 1 { //获取随机基准值 let elme = list[rand::thread_rng().gen_range(1, list.len())]; let (mut left, mut right) = (Vec::new(), Vec::new()); //根据基准值比较,排序后的值放在左边还是右边 for num in list.iter_mut() { if *num == elme { continue; } else if *num < elme { left.push(*num); } else { right.push(*num); } } //递归调用分治 let (mut left, mut right) = (quick_sort(&mut left), quick_sort(&mut right)); left.push(elme); left.append(&mut right); //由于无法返回不同的声明周期的Vec,转而求其次,重新赋值 list.truncate(0); //清理 list.append(&mut left); //装弹 } list}# 示例:use rand::Rng;fn main() { let mut list = vec![3, 5, 8, 1, 2, 9, 4, 7, 6]; quick_sort(&mut list); assert_eq!(list, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]);}
性能分析
快速排序的一次划分算法从两头交替搜索,直到low和hight重合,因此其时间复杂度是O(n);而整个快速排序算法的时间复杂度与划分的趟数有关。4
理想的情况是,每次划分所选择的中间数恰好将当前序列几乎等分,经过log2n趟划分,便可得到长度为1的子表。这样,整个算法的时间复杂度为O(nlog2n)。4
最坏的情况是,每次所选的中间数是当前序列中的最大或最小元素,这使得每次划分所得的子表中一个为空表,另一子表的长度为原表的长度-1。这样,长度为n的数据表的快速排序需要经过n趟划分,使得整个排序算法的时间复杂度为O(n2)。4
为改善最坏情况下的时间性能,可采用其他方法选取中间数。通常采用“三者值取中”方法,即比较H->r[low].key、H->r[high].key与H->r[(low+high)/2].key,取三者中关键字为中值的元素为中间数。4
可以证明,快速排序的平均时间复杂度也是O(nlog2n)。因此,该排序方法被认为是目前最好的一种内部排序方法。4
从空间性能上看,尽管快速排序只需要一个元素的辅助空间,但快速排序需要一个栈空间来实现递归。最好的情况下,即快速排序的每一趟排序都将元素序列均匀地分割成长度相近的两个子表,所需栈的最大深度为log2(n+1);但最坏的情况下,栈的最大深度为n。这样,快速排序的空间复杂度为O(log2n)。4


 扫码下载APP
扫码下载APP

 科普中国APP
科普中国APP
 科普中国
科普中国
 科普中国
科普中国