The inflammatory storm: How does the immune system attack itself?科学辟谣 2020-03-23 |
The immune system gets into a mess.
Author | Xu Sijia School of Medicine, Kyoto University, Japan
It’s delighted that the confirmed cases of COVID-19 have been declining outside Hubei Province in recent days. Meanwhile, the overall death cases are increasing, which have exceeded 2000 in February 19. Some patients don’t show specific and severe symptoms in early diagnosis, however, the development of pathogenic condition is extremely dangerous, making the treatment very difficult.
Many experts said in interviews: for those patients with poor prognosis, not only their lung suffers damage, but also their other organs including liver and kidney are threatened by the deteriorated condition. At the press conference held by the State Council on February 15, Zhou Qi, an academician from the Chinese Academy of Science, specifically mentioned the fatal impact caused by the inflammatory storm (or cytokine storm).
What is the inflammatory storm (or cytokine storm)? How does it exacerbate the symptom and cause death? Let’s have a brief discussion here.
The inflammation: Making our immune system better again
Let’s start with the general inflammation. The human immune system is just like a highly-organized military because each part has defined functions. For example, it attacks foreign bodies and rejuvenates the damage; it also identifies your body’s own cells to maintain a stable internal environment.
When being attacked, the immune system would respond to the pathogen. The more serious the pathogen is, the stronger the immune system responds. Once the immune response causes a vascular damage and local tissue injury, the inflammation would appear.
Any factors that can cause injury could result in inflammation, both infectious and non-infectious. For example, non-infectious inflammation could be induced by substances other than pathogens (such as medicines, foreign bodies and the debris of the human necrotic tissue).
The inflammatory response is frequently occurred in daily life. For example, when our finger was cut by kitchen knife, the bacteria hidden in knife would invade into our body through the wound. If we don’t disinfect the wound quickly, it may easily become infected, and then your already painful wound would become febrile, which is a symptom of local vasodilatation; it may become swollen, and this is due to the increased vascular permeability, the components of the blood exuding from blood vessel wall would enter the infected tissue; some suppuration may appear in your wound, which are the combination of white blood cells and the dead pathogens.

Cutting your fingers by accident may cause an acute inflammatory. | unsplash
The protective inflammatory responses include vasodilation, increased vascular permeability, and accumulation of white blood cells in infected areas.
However, we may wonder that how the immune cells that are transported with the blood recognize the infected wound and aggregate to the target area? This comes to "cytokines".
Once being infected, immune cells near the affected area, such as macrophages which are always active in tissues, will be activated and release polypeptides called “cytokines.” Some of them promote inflammation, and others eliminate inflammation.
In the early phase of inflammation, pro-inflammatory cytokines play the major role, which could attract immune cells from elsewhere to aggregate here. Those aggregated immune cells will be activated and produce more cytokines to attract more immune cells until they are enough to eliminate the pathogen. (It can be concluded that the intensity of inflammatory response could be enhanced by the increasing number of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
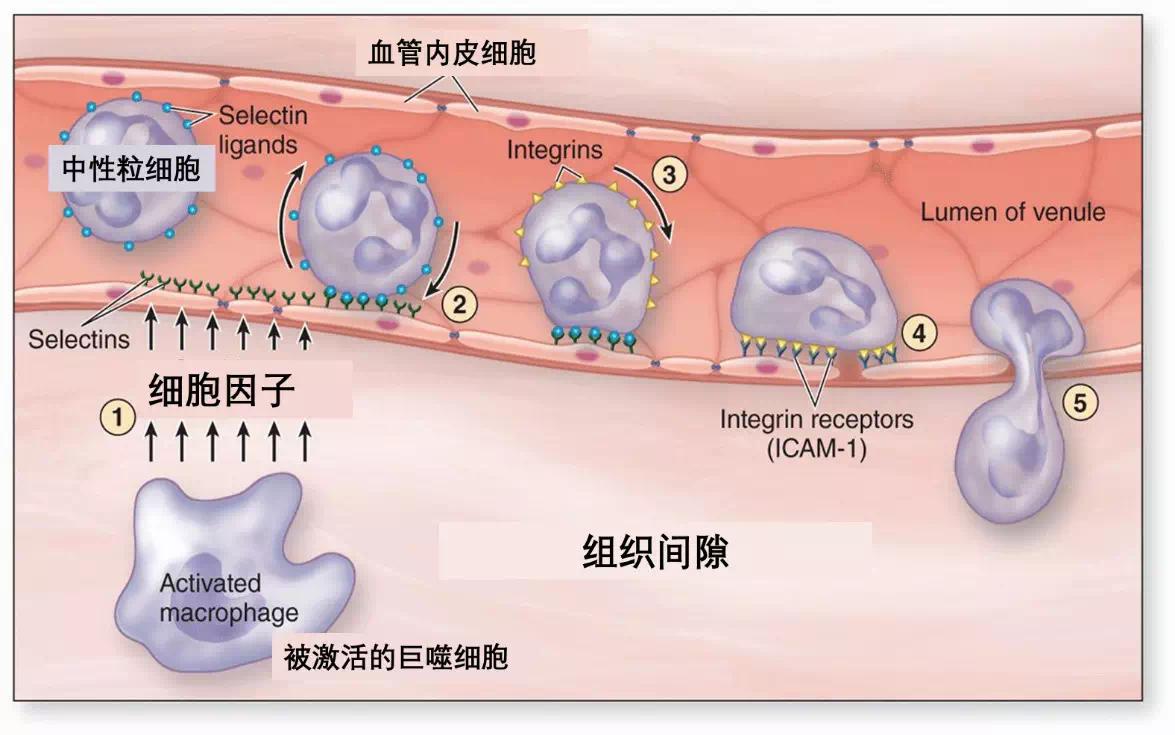
Immune cells ("neutrophils" in the figure) leave the blood vessels walls and enter the infected area driven by cytokines released from macrophages (2-3-4-5 sequentially shows the process of neutrophils leaving from the blood vessels walls) | basicmedicalkey.com
Inflammation is a double-edged sword. On the one hand, immune cells can attack foreign bodies, promote the rejuvenation of tissue and maintain the internal environment; on the other hand, they may not always attack the pathogen exactly and often difficult to identify the true foreign bodies once being activated, which will damage the normal tissue.
The necrotic human tissues will release substances such as nucleic acid and heat shock protein 70. Since these substances don’t commonly exist outside the cell, they will be recognized as foreign bodies, promoting the inflammatory responses and causing increasing damage to the tissue.
Therefore, the inflammatory responses should be accurately controlled, which enable the released cytokines and the aggregated immune cells to keep up with the intensity of infection.
If it is out of control—
The immune cells are releasing cytokines. | creative-biolabs.com
The Inflammatory storm: Self-attacking caused by immunity dysfunction
The inflammatory storm is also called "cytokine storm", which is an over-reaction immune response.
When cytokines are over-produced for any reason, they will enter the systemic circulation and activate a large number of immune cells throughout the body, causing a wide range of acute inflammatory. If not being properly handled, patient’s condition will begin to decline sharply.
Because the immune system is fully activated, they totally release all the anti-pathogen substances, which attack other healthy organs at the same time, resulting in the failure of multiple organs. For example, the COVID-19 infects lungs and then triggers immune responses. Multiple immune cells and exudates accumulate in lungs, which affects the lung. The obstructive airway will aggravate the hypoxia symptoms, causing acid-base disorder.
Excessive immune response could cause heart damage and trigger acute myocarditis. The early symptoms of this disease could be mistaken as cold, such as fever, fatigue, and runny nose, which is difficult to diagnose when mixed with the symptom of COVID-19. However, the rapid progress of pathogenic condition can cause the sudden cardiac arrest, which is a major incentive of sudden manhood death. In addition, recent research stated that clinical patients with new coronavirus pneumonia show varying intensity of liver and kidney damage and intestinal inflammation.
Excessive immune response could also cause damage to the blood vessels. Immune cells will initially damage the inner wall of blood vessels, allowing inflammatory substances to infiltrate other structures and tissues, which distend the inflammation. Along with the necrosis of vascular endothelial cells, they will release the nitric oxide free radical with high activity, triggering a second attack on the blood vessel walls. What’s worse, the exposure of various structures under the damaged endothelium will activate blood coagulation factors, cause the abnormal platelet aggregation, and then damage coagulation, which could result in serious symptoms such as internal hemorrhage and circulatory shock.
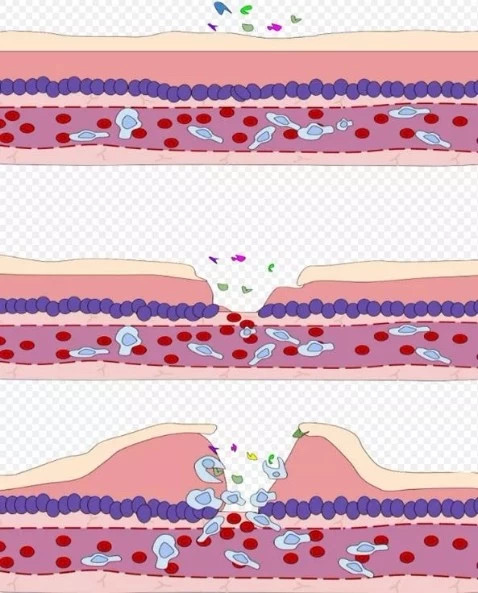
Cells and inflammatory substances exude after vascular injury. | commons.wikimedia.org
Together, the inflammatory storm is an important transitional point from mild to severe and critically ill. Once the uncontrolled inflammation begins to spread throughout the whole body, the body is just like immersed in a sea of inflammatory substances including cytokines, oxygen free radicals, blood coagulation factors and necrotic tissues. Meanwhile, the increasingly severe damage to other organs will increasing the difficulty of treatment, which is also a major cause for the death of severe and critically ill patients.
The tragedy in history: Excessive inflammatory responses caused by anticancer drugs.
Just like the general inflammation, the causes for the inflammatory storm are varied, which could be infectious or non-infectious. From the clinical manifestation, the inflammatory storm could be systemic infection at the beginning, or it could be topical infection and then evolve into systemic infection. The latter is more common.
Once the human body being attacked by a totally new and strong pathogenic pathogen (such as COVID-19), it will trigger an excessive immune response and activate multiple immune cells in the same area, adding the risks of triggering inflammatory storms. After the first attack, the body usually has a short steady period. However, the recurring symptoms later will aggravate the condition, causing continuous damage to the body.
The inflammatory storm is just like tornadoes caused by “butterfly effect”. | audrageras.com
In addition to exogenous infection, the causes for endogenous infections have also received much attention in recent years. For example, there are always many microorganisms in human intestine. Normally, rather than triggering disease, they could produce vitamins for human use. When the patients suffer severe injury or acute infection, the body’s stress response could destroy intestinal barrier, causing the translocation of intestinal microbiota. The patient’s condition may show a marked improvement after treatment, but the imbalance of intestinal microbiota and declined immunity may trigger a second excessive inflammatory response, causing inflammatory storm.
Certainly, there also exists non-infections condition, such as the therapy of some experimental drug. And the anticancer drugs deserve our attention.
It’s a fact that cytokines can mobilize immune cells to attack foreign bodies. In the 1990s, scientists tried to treat tumors (cancer) based on this principal, but didn’t get expected results. What is the reason behind that?
There exists one kind of immune cell called “killer T cell” (also named cytotoxic T cell), which could exert strong impact on the tumors and kill them. Only after another immune cell called “helper T cell” firstly identified the foreign bodies and released the cytokines, did the strong cytotoxic T cell begin to be activated and attack foreign bodies.
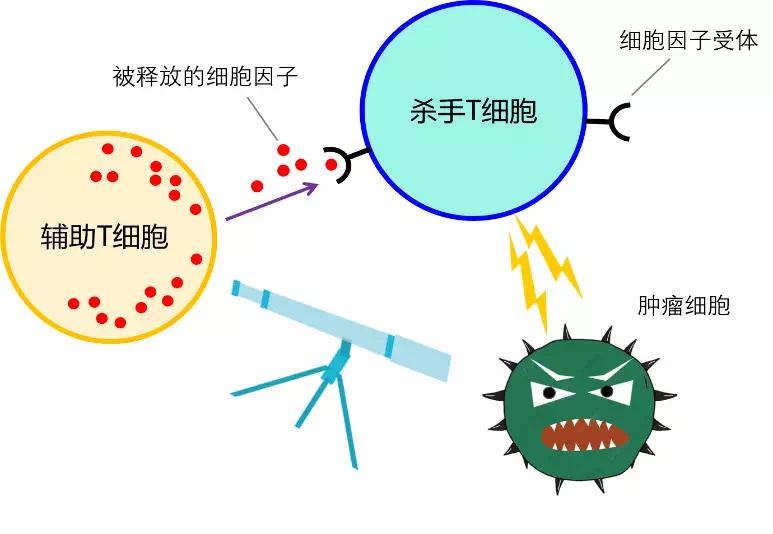
Helper T cells (left) firstly identify the foreign bodies, and then release the cytokines to activate killer T cells (top right) | From the author
Killer T cells generally remain inhibited and can’t kill tumor cells initiatively. Therefore, human intervention is needed to activate them. Scientific research found that a cytokine called IL-12 can activate a strong response from helper T cells, and then stimulate a large number of killer T cells. This is certainly a good news for cancer treatment.
In a 1995 clinical trial, scientists injected 17 patients with kidney cancer with IL-12 cytokines. Unfortunately, 12 of them were urgently sent to hospital due to an acute inflammatory storm, and finally 2 of them died. Therefore, the immunity mechanism is not as simple as people expected. Even in 21st century, the complication of inflammatory storm is an uncharted area in tumor immunotherapy.
Views on the outbreak of COVID-19: The high-risk group of inflammatory storm and way to deal with it
What should we focus in the outbreak of COVID-19? Which groups are at high-risk to be infected? And how we deal with it?
Starting from patients themselves, those who have basic disease such as coronary heart disease, diabetes and renal Insufficiency are more likely to trigger aggravated condition and cause multiple organ dysfunctions. According to an announcement from the American College of Cardiology (AAC) on February 15, patients with basic disease are more likely to trigger complications or have higher mortality rate after infection with COVID-19; more than 50% of inpatients have chronic illnesses; 40% confirmed cases have a cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
In addition, compared with the elderly and children, young adults always have more severe response to the inflammatory storm. It means that since young adults generally have stronger immunity, they are at higher risks to trigger excessive immune responses.
The clinical symptoms vary between individual differences. That’s because different people will show various symptoms in different phases of the disease.
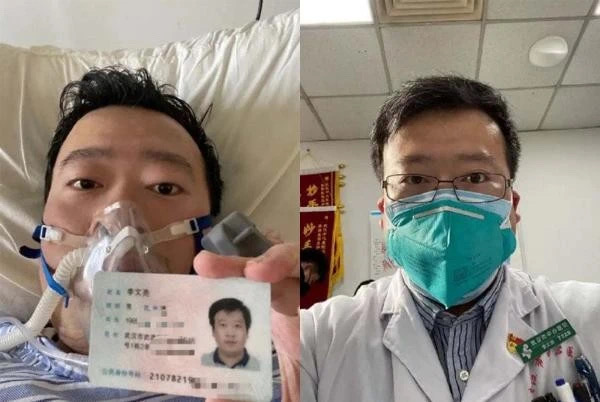
The heart breaking news that young Dr.Li Wenliang passed away on February 6 shocked many people. | From the Internet
In clinical practice, there is no specific method to deal with the inflammatory storms, and the mainly-applied methods are non-specific combination therapy including anti-infective treatment, anti-inflammatory treatment assisted by glucocorticoids, nutritional support and artificial ventilation. (Glucocorticoids are commonly used in clinical anti-inflammatory drugs, which are also contained in the many ointments that people apply to the skin to treat eczema.)
Based on the concept of the inflammatory storm (systemic excessive inflammatory response), active anti-inflammatory treatment seems to be an appropriate method. But the clinical treatment doesn’t achieve satisfactory results. In recent years, people have gradually realized that in the late phase of the inflammatory storm, excessive immune response is accompanied by declined immune function. Is it paradox?
The cytokines is still the key factor to explain, which could be both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory. Generally, this function could help the body to regulate the inflammation to keep up with the actual intensity of infection
When the mild symptom is aggravated into severe symptom caused by the inflammatory storm, the body’s tissue would be seriously damaged. The cytokines, both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory, enter the systemic circulation, triggering an extremely complicated immune dysfunction. The inflammatory response will be aggravated, and at the same time, the weaken recognition and phagocytosis of pathogens will lead to a decline in immunity.
Treatment can’t be totally focused on suppressing inflammatory response when dealing with the inflammatory storms. It is very difficult to treat it because the involvement of multiple organs and other complications. And the inflammatory storm is the principal cause for death in the outbreak of SARS, MERS, and flu.
Experts are trying to screen out drugs to inhibit the inflammatory storm. Test drugs include traditional drugs which have been proven to “effectively inhibit the inflammatory cytokines in treating rheumatism. And some of the drugs have been put into clinical trials.
The prevention and following treatment of the inflammatory storms will certainly become the focus in the treatment of COVID-19. This passage definitely helps you know more about your body.
(Editor Gao Peiwen)
References:
[1]. Cohen, Jon. "IL-12deaths: explanation and a puzzle." Science270.5238 (1995): 908-908.
[2].Cardiac Implications of Novel Wuhan Coronavirus (COVID-19)-American College of Cardiology
[3].https://www.quora.com/What-is-a-cytokine-storm-and-what-are-the-diseases-that-cause-that/answer/Tirumalai-Kamala
[4].《急危重症病理生理学》,姚永明,科学出版社,2013。
责任编辑:王超
 科普中国APP
科普中国APP
 科普中国微信
科普中国微信
 科普中国微博
科普中国微博

最新文章
-
为何太阳系所有行星都在同一平面上旋转?
新浪科技 2021-09-29
-
我国学者揭示早期宇宙星际间重元素起源之谜
中国科学报 2021-09-29
-
比“胖五”更能扛!我国新一代载人运载火箭要来了
科技日报 2021-09-29
-
5G演进已开始,6G研究正进行
光明日报 2021-09-28
-
“早期暗能量”或让宇宙年轻10亿岁
科技日报 2021-09-28
-
5G、大数据、人工智能,看看现代交通的创新元素
新华网 2021-09-28












微信扫一扫:分享
微信里点“发现”,扫一下
二维码便可将本文分享至朋友圈。