后序遍历(LRD)是二叉树遍历的一种,也叫做后根遍历、后序周游,可记做左右根。后序遍历有递归算法和非递归算法两种。在二叉树中,先左后右再根,即首先遍历左子树,然后遍历右子树,最后访问根结点。
定义后序遍历首先遍历左子树,然后遍历右子树,最后访问根结点,在遍历左、右子树时,仍然先遍历左子树,然后遍历右子树,最后遍历根结点。即:
若二叉树为空则结束返回,
否则: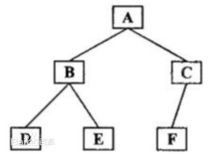 (1)后序遍历左子树
(1)后序遍历左子树
(2)后序遍历右子树
(3)访问根结点
如右图所示二叉树
后序遍历结果:DEBFCA
已知前序遍历和中序遍历,就能确定后序遍历。1
递归算法算法1/*public class BTNode //二叉树节点类型{ public BTNode lchild; public BTNode rchild; public char data;}*//*public string btstr //全局变量*/public string postOrder(BTNode t){ btstr=""; postOrder1(r); returen btstr;}public string postOrder1(BTNode t){ if(t!=null) { postOrder(t.lchild); postOrder(t.rchild); bstr+=t.data.ToString()+" "; }}算法2PROCEDURE POSTRAV(BT)IF BT0 THEN{ POSTRAV(L(BT)) POSTRAV(R(BT)) OUTPUT V(BT)}RETURN算法3struct btnode { int d; struct btnode *lchild; struct btnode *rchild;};void postrav(struct btnode *bt) { if(bt!=NULL) { postrav(bt->lchild); postrav(bt->rchild); printf("%d ",bt->d); }}算法4procedure last(bt:tree);begin if btnil then begin last (bt^.left); last (bt^.right); write(bt^.data); end;end;算法5public classTreeNode{ intval; TreeNodeleft; TreeNoderight; TreeNode(intx){ val = x; }}public void postOrder(TreeNode biTree){ TreeNode leftTree = biTree.left; if (leftTree != null) { postOrder(leftTree); } TreeNode rightTree = biTree.right; if(rightTree != null){ postOrder(rightTree); } System.out.printf(biTree.val+"");}非递归算法核心思想首先要搞清楚先序、中序、后序的非递归算法共同之处:用栈来保存先前走过的路径,以便可以在访问完子树后,可以利用栈中的信息,回退到当前节点的双亲节点,进行下一步操作。
后序遍历的非递归算法是三种顺序中最复杂的,原因在于,后序遍历是先访问左、右子树,再访问根节点,而在非递归算法中,利用栈回退到时,并不知道是从左子树回退到根节点,还是从右子树回退到根节点,如果从左子树回退到根节点,此时就应该去访问右子树,而如果从右子树回退到根节点,此时就应该访问根节点。所以相比前序和后序,必须得在压栈时添加信息,以便在退栈时可以知道是从左子树返回,还是从右子树返回进而决定下一步的操作。2
算法1void postrav1(struct btnode* bt){ struct btnode* p; struct { struct btnode* pt; int tag; }st[MaxSize]; int top=-1; top++; st[top].pt=bt; st[top].tag=1; while(top>-1)/*栈不为空*/ { if(st[top].tag==1)/*不能直接访问的情况*/ { p=st[top].pt; top--; if(p!=NULL) { top++;/*根结点*/ st[top].pt=p; st[top].tag=0; top++;/*右孩子结点*/ st[top].pt=p->p->rchild; st[top].tag=1; top++;/*左孩子结点*/ st[top].pt=p->lchild; st[top].tag=1; } } if(st[top].tag==0)/*直接访问的情况*/ { printf("%d",st[top].pt->d); top--; } } }算法2void postrav2(struct btnode* bt){ struct btnode* st[MaxSize],*p; int flag,top=-1; if(bt!=NULL) { do { while(bt!=NULL) { top++; st[top]=bt; bt=bt->lchild; } p=NULL; flag=1; while(top!=-1&&flag) { bt=st[top]; if(bt->rchild==p) { printf("%d",bt->d); top--; p=bt; } else { bt=bt->rchild; flag=0; } } }while(top!=-1) printf("\n"); }}本词条内容贡献者为:
王伟 - 副教授 - 上海交通大学


 扫码下载APP
扫码下载APP

 科普中国APP
科普中国APP
 科普中国
科普中国
 科普中国
科普中国